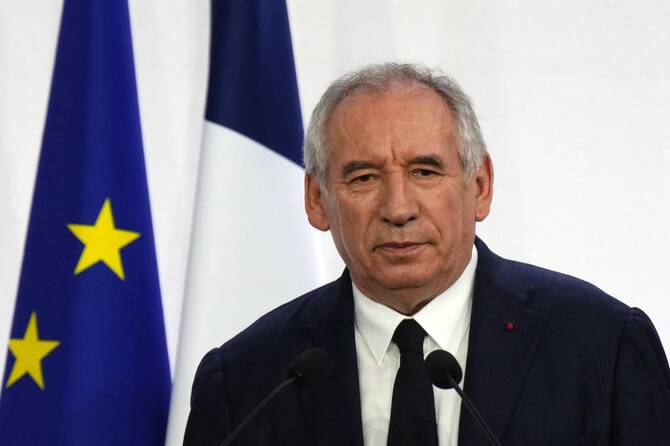
France found itself mired in yet another crisis on Tuesday, after Prime Minister Francois Bayrou’s gamble to win backing for his deeply unpopular debt-reduction plan backfired, plunging the country deeper into political and financial instability.
French markets tumbled after Bayrou jolted the political establishment out of its summer slumber on Monday with his unexpected move to seek a September 8 confidence vote on his debt-cutting plan. His proposal was roundly rejected by opposition parties, who said they would relish the opportunity to cut short his minority government’s time in office.
In a symbolic moment that underlined his predicament, Bayrou tripped and nearly went flying as he took to the stage on Tuesday to deliver his first comments since the previous night’s announcement. He said lawmakers must now choose between “chaos” and “responsibility,” and urged the French to pressure their representatives to make a prudent choice ahead of September 8.
“I am not asking anyone to change his mind but one can think it over,” Bayrou later told journalists.
If Bayrou falls, Macron could dissolve parliament and hold fresh legislative elections — a move he has previously rejected — or install a new government. However, neither course of action is likely to solve France’s budget issues or political gridlock.
A source in a key ministry said they expected Macron to opt for a new prime minister.
“The French prime minister’s decision to call an early vote of confidence is most likely to trigger his replacement with yet another prime minister or (less likely) fresh legislative elections,” Capital Economics analysts wrote.
“Either way, France’s budget deficit will remain well above the level needed to stabilize the debt ratio.”
Interior Minister Bruno Retailleau, who leads the conservative Republicans, said it would be “irresponsible” and “against France’s interests” to vote for the government to fall.
Others disagreed.
The far-right National Rally, led by Marine Le Pen, said it wants Macron to call a snap parliamentary election.
“I don’t see what new prime minister wouldn’t be immediately censured,” a source close to Le Pen told Reuters.
The Socialists, whose vote will be crucial, also said they would vote against Bayrou.
“We need a different prime minister and, above all, a different policy,” lead Socialist lawmaker Boris Vallaud wrote on X.
The confidence vote will be held two days before protests called by various groups on social media and backed by leftist parties and some unions, recalling the Yellow Vest unrest that erupted in 2018 over fuel price hikes and the cost of living.
“Unless Francois Bayrou is confirmed in office — which is a hypothesis today that appears unlikely — we will enter a new phase which will be a phase of destabilization,” said pollster Jean-Daniel Levy, predicting negative consequences for the economy and France’s image abroad.
What next?
A source close to Bayrou said his government was open to negotiation on the details of his budget proposals, though they were adamant that a budget squeeze is necessary.
Bayrou said on Tuesday he would ask high-income taxpayers to make a special effort to help curb the deficit.
Bayrou knew a no-confidence vote would eventually be tabled over the budget and decided to get ahead of the opposition, the source said. France’s blue chip CAC40 index was down 1.5 percent on Tuesday, having fallen 1.6 percent late on Monday. Banking giants BNP Paribas and Societe Generale slid more than 6 percent each.
Meanwhile, 10-year French government bond yields briefly rose to 3.53 percent, the highest since March, before steadying at 3.50 percent. When a bond’s yield rises, its price falls.